مرحله چهارم :تعیین ریتم
STEP 4 (Asses Rhythm)
ابتدا برای تعیین ریتم، لیدهای اندامی را بررسی می کنیم . اگر معیارهای زیر مشاهده شد ریتم سینوسی نرمال است( البته بهترین لید برای بررسی ریتم لید II می باشد.به همین علت در اغلب نوار قلبها، لید Long II گرفته می شود.)
الف-ریتم سینوسی نرمال (NSR):
ü موج P در I,II,aVF مثبت و درaVR منفی باشد.
ü به دنبال هر P، کمپلکس QRS وجود داشته باشد.
ü ریت بین 100ـ60 در دقیقه باشد.
ü اگر ریتم این ویژگیها را نداشت، ریتم سینوسی نرمال نخواهد بود.
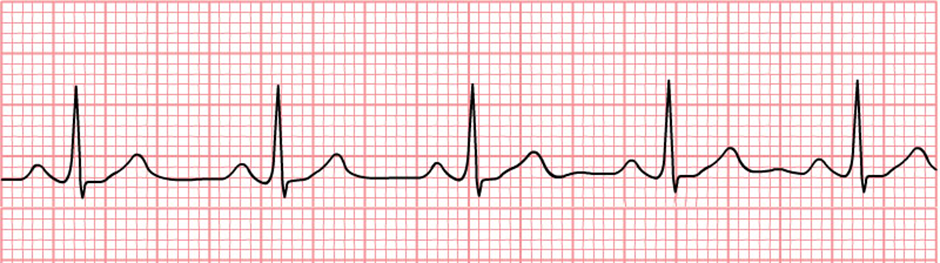
شکل 1- ریتم سینوسی نرمال
ب –ریتم غیر سینوسی ( بررسی آریتمی ها):
در صورت طبیعی نبودن ریتم، این 7 مرحله را برای بررسی ریتم استفاده می کنیم:
1-آیا تاکیکارد است یا برادیکارد : ریت بین 100-60 نرمال است .ریت بالای 100 تاکیکاردی و ریت زیر 60 برادیکاردی است.
2-شکل QRS : منظم یا نامنظم است ، اگرنامنظم است میزان نامنظمی چقدر است؟
( If irregular is it regularly irregular or irregularly irregular?)
3-دیوریشن QRS :
Narrow complex: sinus, atrial or junctional origin.
Wide complex: ventricular origin, or supraventricular with aberrant conduction.
4- آیا Pوجود دارد یا نه ؟
Absent: sinus arrest, atrial fibrillation
Present: morphology and PR interval may suggest sinus, atrial, junctional or even retrograde from the ventricles.
5- ارتباط بین P و QRS چگونه است ؟
· AV association (may be difficult to distinguish from isorhythmic dissociation)
· AV dissociation:
- complete: atrial and ventricular activity is always independent.
o incomplete: intermittent capture.
6- شروع و ختم آریتمی چگونه است؟
· Abrupt: suggests re-entrant process.
· Gradual: suggests increased automaticity.
7- پاسخ به مانورهای واگ چگونه است؟
- Sinus tachycardia, ectopic atrial tachycardia: gradual slowing during the vagal manoeuvre, but resumes on cessation.
- AVNRT or AVRT: abrupt termination or no response.
- Atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter: gradual slowing during the manoeuvre.
- VT : no response
Differential Diagnosis
Narrow Complex (Supraventricular) Tachycardia
ATRIAL – REGULAR
- Sinus tachycardia
- Atrial tachycardia
- Atrial flutter
- Inappropriate sinus tachycardia
- Sinus node re-entrant tachycardia
ATRIAL – IRREGULAR
ATRIOVENTRICULAR
- Atrioventricular re-entry tachycardia (AVRT)
- AV nodal re-entry tachycardia (AVNRT)
- Automatic junctional tachycardia
Wide Complex Tachycardia (WCT)
REGULAR WCT
- Ventricular tachycardia
- Antidromic atrioventricular re-entry tachycardia (AVRT).
- Any regular supraventricular tachycardia with aberrant conduction — e.g. due to bundle branch block, rate-related aberrancy.
Note: All regular WCTs should be considered to be VT until proven otherwise.
IRREGULAR
- Ventricular fibrillation
- Polymorphic VT
- Torsades de Pointes
- AF with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome
- Any irregular supraventricular tachycardia with aberrant conduction — e.g. due to bundle branch block, rate-related aberrancy.
Bradycardia
P WAVES PRESENT
1. Every P wave is followed by a QRS complex (= sinus node dysfunction)
2. Not every P wave is followed by a QRS complex (= AV node dysfunction)
- AV block: 2nd degree, Mobitz I (Wenckebach)
- AV block: 2nd degree, Mobitz II (Hay)
- AV block: 2nd degree, “fixed ratio blocks” (2:1, 3:1)
- AV block: 2nd degree, “high grade AV block”
- AV block: 3rd degree (complete heart block)
P WAVES ABSENT
- Narrow complex: Junctional escape rhythm
- Broad complex: Ventricular escape rhythm
For escape rhythms to occur there must be a failure of sinus node impulse generation or transmission by the AV node.


